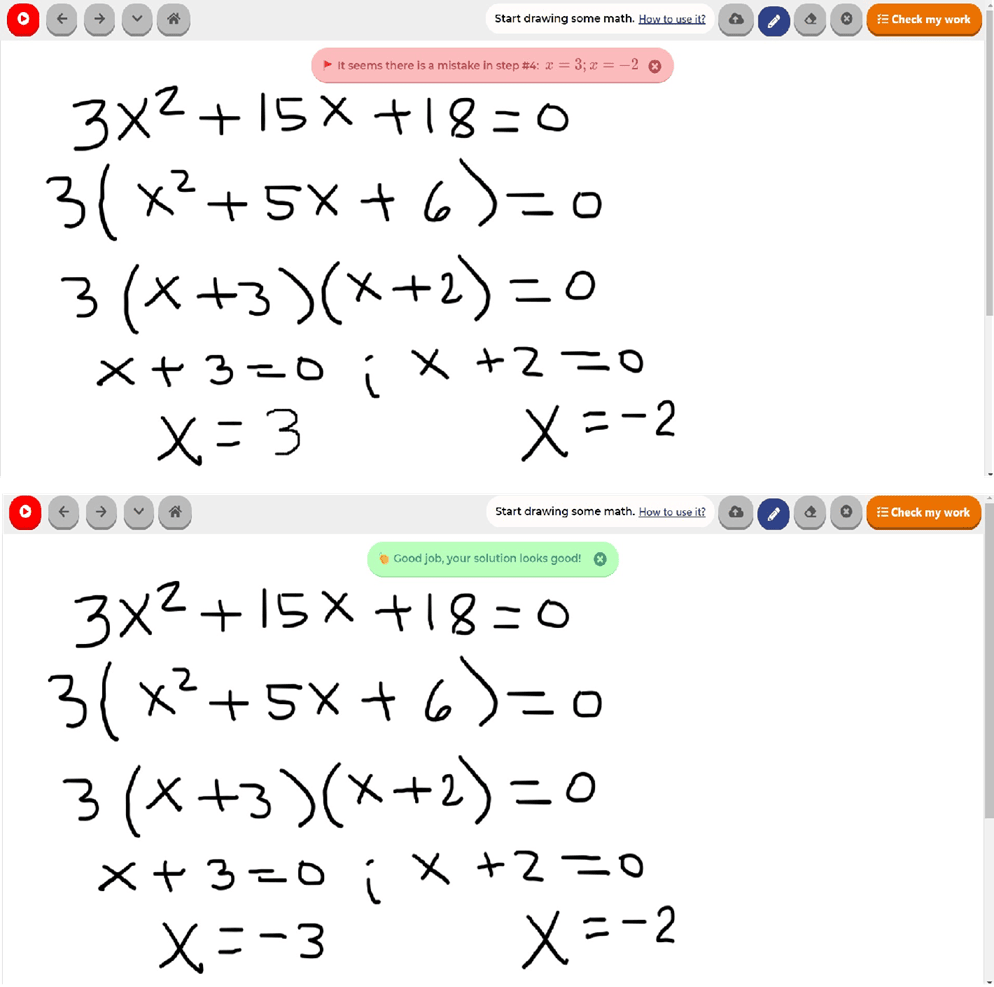
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Choose an option
- Exact Differential Equation
- Linear Differential Equation
- Separable Differential Equation
- Homogeneous Differential Equation
- Integrate by partial fractions
- Product of Binomials with Common Term
- FOIL Method
- Integrate by substitution
- Integrate by parts
- Load more...
We can identify that the differential equation $y\left(\ln\left(x\right)-\ln\left(y\right)\right)dx=\left(x\ln\left(x\right)-x\ln\left(y\right)-y\right)dy$ is homogeneous, since it is written in the standard form $M(x,y)dx+N(x,y)dy=0$, where $M(x,y)$ and $N(x,y)$ are the partial derivatives of a two-variable function $f(x,y)$ and both are homogeneous functions of the same degree
Learn how to solve problems step by step online.
$y\left(\ln\left(x\right)-\ln\left(y\right)\right)dx=\left(x\ln\left(x\right)-x\ln\left(y\right)-y\right)dy$
Learn how to solve problems step by step online. Solve the differential equation y(ln(x)-ln(y))dx=(xln(x)-xln(y)-y)dy. We can identify that the differential equation y\left(\ln\left(x\right)-\ln\left(y\right)\right)dx=\left(x\ln\left(x\right)-x\ln\left(y\right)-y\right)dy is homogeneous, since it is written in the standard form M(x,y)dx+N(x,y)dy=0, where M(x,y) and N(x,y) are the partial derivatives of a two-variable function f(x,y) and both are homogeneous functions of the same degree. Use the substitution: x=uy. Expand and simplify. Integrate both sides of the differential equation, the left side with respect to u, and the right side with respect to y.