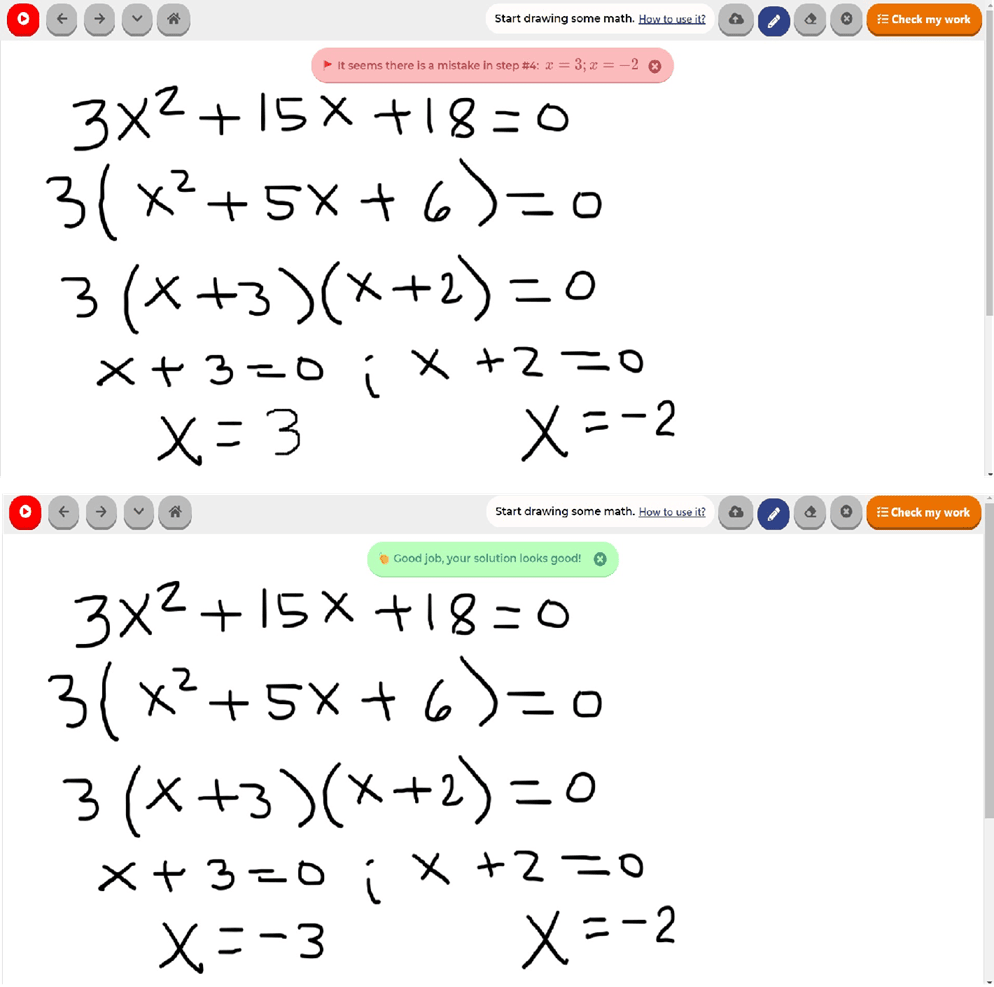
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Choose an option
- Solve using L'Hôpital's rule
- Solve without using l'Hôpital
- Solve using limit properties
- Solve using direct substitution
- Solve the limit using factorization
- Solve the limit using rationalization
- Integrate by partial fractions
- Product of Binomials with Common Term
- FOIL Method
- Load more...
The trinomial $\left(x^2-2x+1\right)$ is a perfect square trinomial, because it's discriminant is equal to zero
Learn how to solve limits by rationalizing problems step by step online.
$\Delta=b^2-4ac=-2^2-4\left(1\right)\left(1\right) = 0$
Learn how to solve limits by rationalizing problems step by step online. Find the limit of ((x+4)(x^2-2x+1))/(2x^(1/2)-2) as x approaches 1. The trinomial \left(x^2-2x+1\right) is a perfect square trinomial, because it's discriminant is equal to zero. Using the perfect square trinomial formula. Factoring the perfect square trinomial. Factor the polynomial 2\sqrt{x}-2 by it's greatest common factor (GCF): 2.