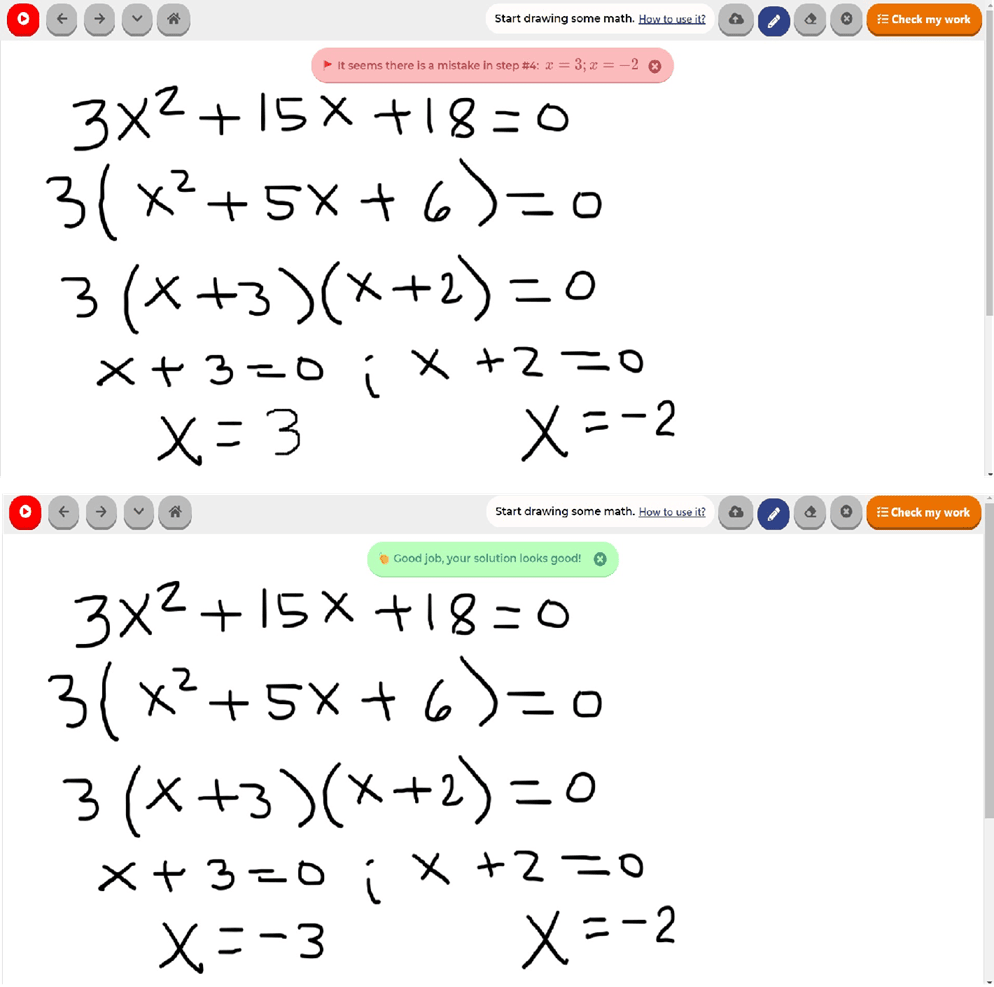
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
The sum of two terms multiplied by their difference is equal to the square of the first term minus the square of the second term. In other words: $(a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2$.
The sum of two terms multiplied by their difference is equal to the square of the first term minus the square of the second term. In other words: $(a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2$.
Solving a math problem using different methods is important because it enhances understanding, encourages critical thinking, allows for multiple solutions, and develops problem-solving strategies. Read more
The difference of two squares is a squared number subtracted from another squared number. Every difference of squares may be factored according to the identity a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b) in elementary algebra.
Get a preview of step-by-step solutions.
Get 3 free complete solutions daily when you signup with your student or academic email.
Earn solution credits, which you can redeem for complete step-by-step solutions.
Save your favorite problems.
Become premium to access unlimited solutions, downloads, discounts and more!